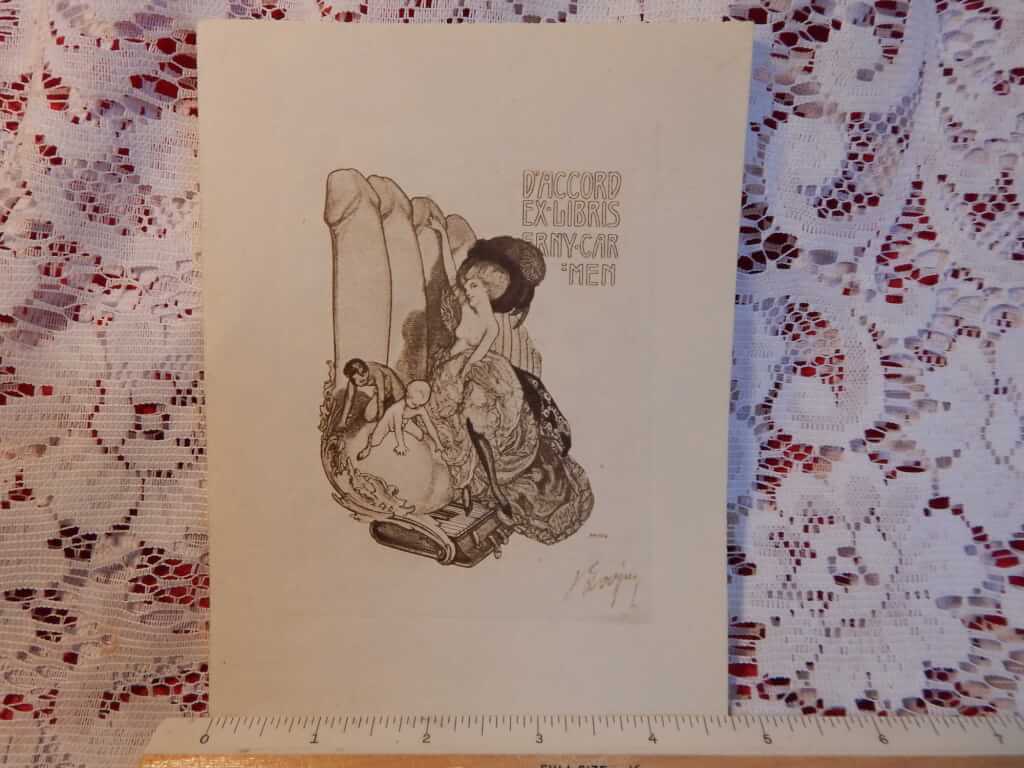
The Autobiography of a Flea, told in a hop, skip, and jump: Recounting all his Experiences of the Human, and Superhuman, Kind, both Male and Female; with his Curious Connections, Backbitings, and Tickling Touches; the whole scratched together and arranged for the Delectation of the Delicate, and for the Information of the Inquisitive. annonymous [disputed but believed to be Stanislas de Rodes, a London lawyer] ("Published by the Authority of The Phlebotomical Society, Cytheria, 1789 [a false imprint, according to Mendez, most likely printed by A. Lefevre (Brussels) for Mlle. Doucé (Paris) c.1890. It is possible that Charles Carrington introduced Doucé to the book as he just arrived in Paris (exiled from England).])
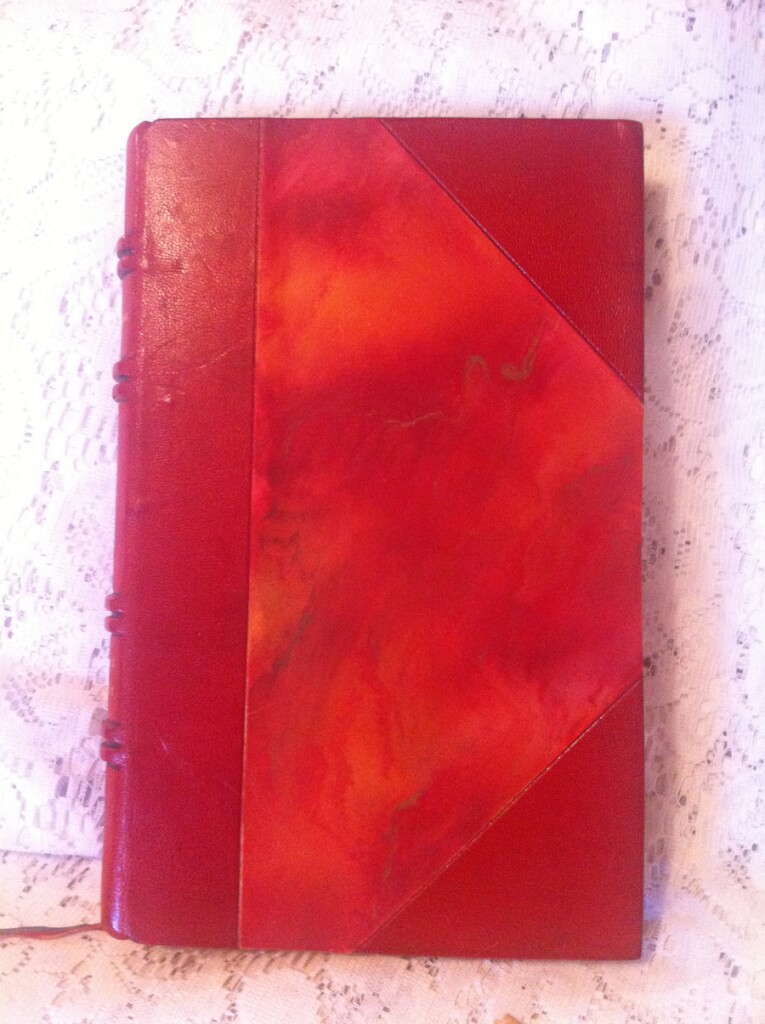
4.75" x 7.75", 190pp, full red Moroccan leather with gilt boarders, 5 raised bands, gilt decorations and title on spine, gilt decorations border paste-downs, top edge gilt, no illustrations present, text decorations throughout, boards loose, signatures loose, some pages detached. A good copy of a VERY rare fine-binding edition of a very rare book. I can find no other copies for sale or in WorldCat.
Written from the point of view of a very observant flea, the story is of the exploits of a young girl and a monastery of corrupt monks. The prose is very well written, erotic, and entertaining, with detailed full-length descriptions, good scene setting, and tension buildups. A question hangs over its authorship who has been referred to as ‘un avocat anglais, bien connu a` Londres’ [an advocate well known in London], suggested to be Frederick Popham Pike, the only barrister known to be writing pornography at this time. Other contenders for its authorship include Frederick Hankey, who died in 1882, Henry Spencer Ashbee, and the current favorite, Stanislas de Rodes.
CHARACTERS
The Flea:
The Narrator of the story is a flea whose name is never revealed. The novel begins with the flea asserting that though he gets his living by blood sucking he is "not the lowest of that universal fraternity". The flea further asserts that his intelligence and abilities of observation and communication are comparable to a human, and demurs from any explanation of the cause, adding that he is "in truth a most wonderful and exalted insect". The unusual narrator allows the story to be written from the viewpoint of a character who neither participates in nor necessarily approves of the sex scenes, and the movement of the narrator between the bodies of the different characters allows the action to follow different characters at different times. Despite ostensibly being written from the first person the novel includes descriptions of the feelings and intentions of various characters which seem more fitting with a third person limited omniscient narrator.
Bella:
The main character of the book, Bella, is an orphan who lives with her uncle and aunt. At the beginning of the story she is 14 and is described as being the admired one of all eyes and the desired one of all hearts - at any rate among the male sex. She begins the book sexually naive, but inquisitive.
Charlie:
Very little description is given of Charlie, and after a brief mention in Chapter 3 he ceases to play any part in the story.
Father Ambrose:
A priest aged 45, described as having a handsome face, with jet black eyes and as being short and stout. The narrator says Ambrose's mind is dedicated to the pursuit of lust, and much of the novel's plot is due to his machinations. After initiating Bella into the ways of unrestrained sensuality, and planning to keep her for himself, he is discovered by the Brother Superior and Brother Clement who insist he share Bella with them. Many scenes of multiple acts of all varieties ensue. Ultimately, Ambrose decides to expand the circle of debauchery by insisting Belle involve her friend the fair, innocent Julia Delmont.
Father Clement:
Father Clement is one of the "brothers" of Father Ambrose and is a participant and co conspirator in the seduction of Bella. He is described as ugly and possessed of an absolutely gargantuan penis. A memorable scene occurs when Clement mistakes the bedroom he believes is occupied by Bella, and throws himself on Bella's puritanical and rigid aunt. After initially believing the advances are those of her husband, with whom she has not been intimate in many years, she feels Clement's enormous size, and leaps up. Clement forces her down, and after initial resistance, she succumbs. They are discovered and Clement escapes out the window. Bella's aunt goes progressively insane screaming for the "priest with the big tool".
Plot
The plot begins with Bella in church. As she leaves, Charlie pushes a note into her hand. She reads that it says he will be in their old meeting place at eight o' clock. She meets him in a garden. After some playful conversation, Charlie introduces her to her first sexual experience. Father Ambrose, who had been hiding in the shrubs, surprises them afterward, scolding both of them for their behaviour and threatening to reveal what they have been doing to their guardians. Bella pleads for mercy. Father Ambrose, appearing to relent, tells Bella to meet him in the sacristy at two o'clock the next day and Charlie to meet him at the same time the day after that. Ambrose instructs Bella into a way she may be absolved of her sins and blackmails her into sex with him, lest he tell her guardian what she was up to. Then Ambrose's colleagues, the Fr Superior & Fr Clement, catch them in the act, and they demand equal rights to Bella's favours. And so Bella is introduced to serving the Holy community in a special way.
Despite his promises, Ambrose goes to see Bella's uncle, Monsieur Verbouc and tells of her lewd behaviour. This leads to her uncle, who has long entertained lustful thoughts of his niece, attempting to force himself on Bella. The narrator then intervenes, biting him to put a damper on his ardour.
Next, Father Clement, looking for Bella's room, climbs into the window of Bella's aunt, the pious Madame Verbouc, who had mistaken him for her husband. M. Verbouc then bursts in and his wife realises she's actually been making love to the randy priest.
Bella's friend, Julia Delmont, becomes Ambrose's next target. By now completely corrupted and happy to go along with whatever Ambrose suggests, Bella readily agrees to the Father's next scheme: She will offer herself to Monsieur Delmont, on condition that her face is covered. The trick is that it will not be Bella who lies there, but Delmont's own daughter. Father Ambrose seduces her and says he will come to her by night and make love to her, but she must hide her face.
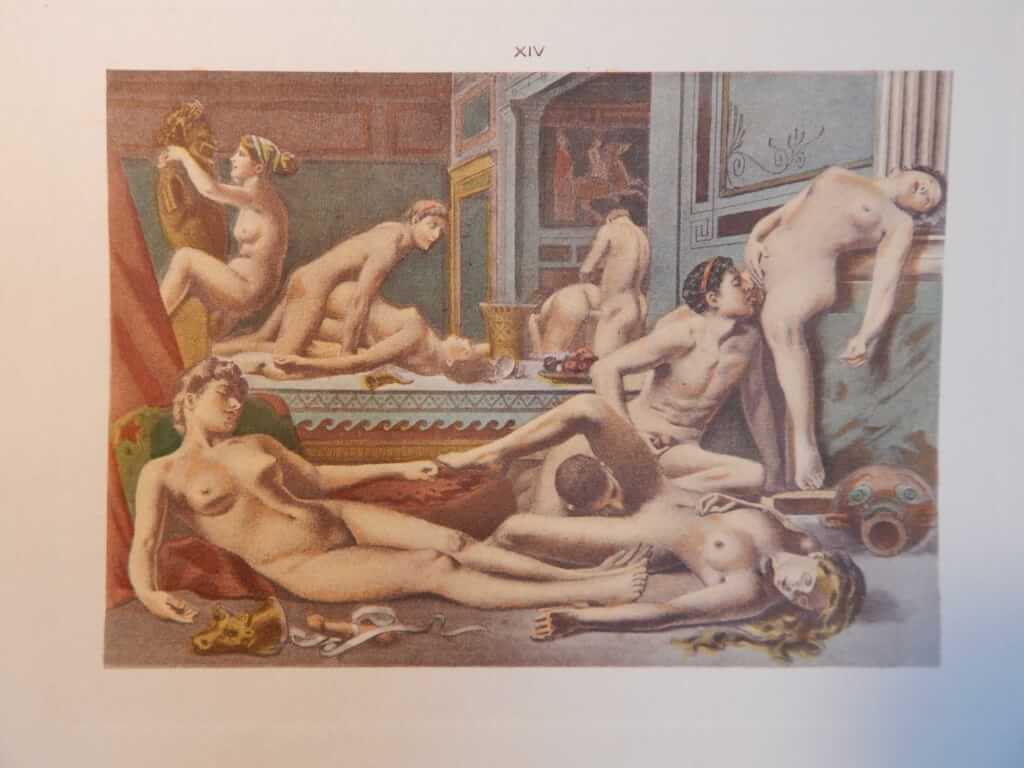
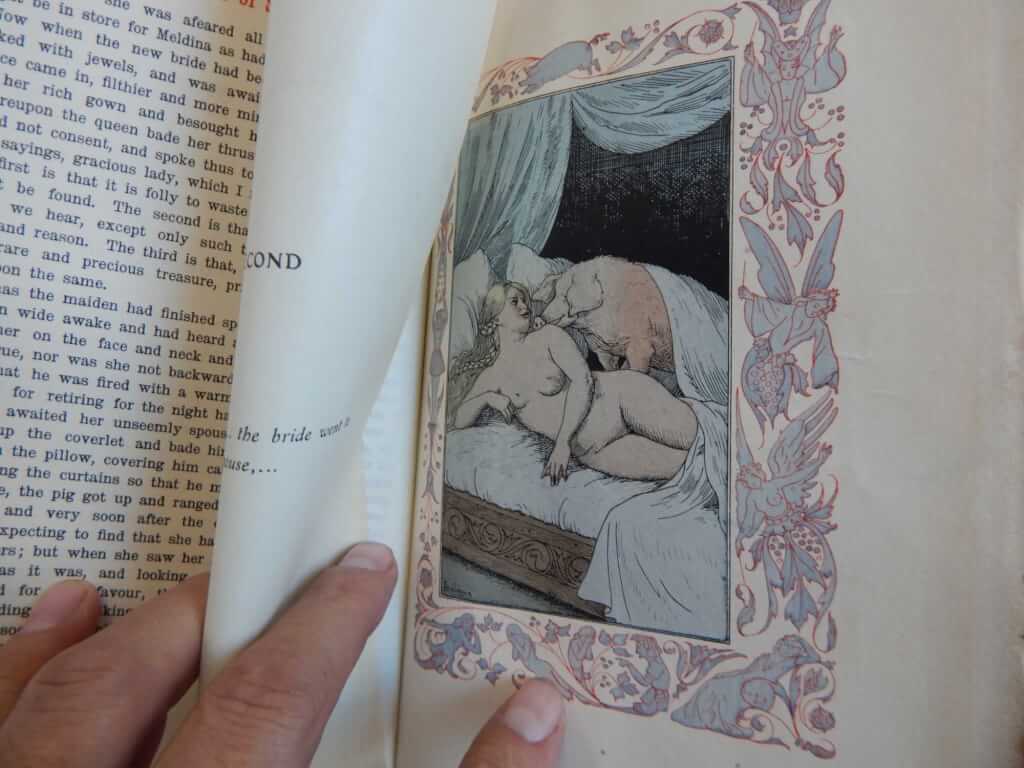
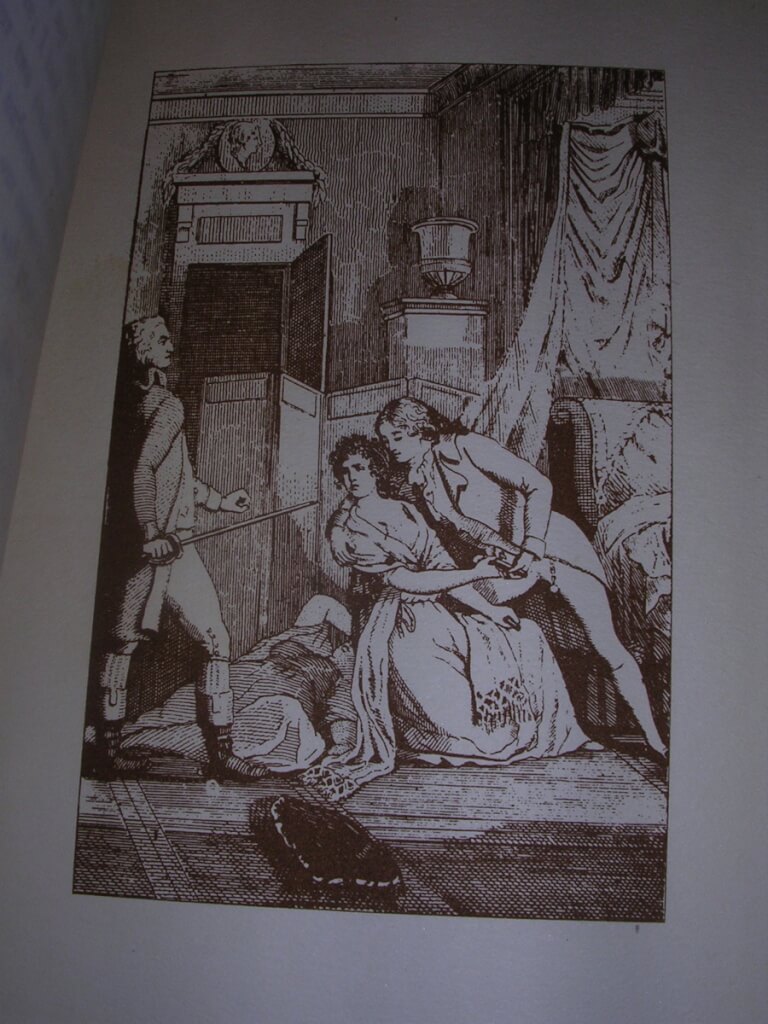
Charming depiction of a drawing room gangbang from the book
When the act is consummated, Bella appears and pretends that it was all a big mistake. But since Delmont has now potentially impregnated his daughter, the only way to be sure his incest cannot be discovered is to have all make love to her as well. In case she is pregnant, nobody can claim that her own father is the father.
Bella and Julia eventually become nuns, and the book ends as they participate in an orgy with 19 priests.